PLANNING WORKS
In engineering services the concept of planning can be defined as methods of providing the highest socio-economic utilization during the construction of appropriate structure through the optimum source in the short, medium and long term. From this point of view it is inevitable to use planning techniques commonly at the each stage of highways construction technology. Planning works usually involve determining that which road is constructed when and with which standards and to define the road network and standards.
 Proper transportation infrastructure investments significantly accelerates the economic progress; however investments with low economic return slow down the speed of progress. Therefore, social and economic surveys gain importance to specify the priorities in the use of resources allocated to General Directorate of Highways. As a result of these surveys, the cost of road and its contribution to the economy of country are looked over with details and then the priorities of the project are specified by regarding the social benefits of road. At the final stage the program is prepared.

In the process of planning transportation basic socio-economic surveys create a work circle over transportation surveys, studies on inventory, estimations, economical analysis and alternatives.
Transportation Surveys:
These surveys are carried on by collecting information about current transportation system, especially on its infrastructure, equipment, analysis of traffic flow, current financial situation of transportation investments and institutional framework.
Studies on Inventory:
It is necessary to gather detailed and correct information about road network in order to realize the works in a healthy way and prepare the most appropriate program. In regular intervals studies are conducted on highways inventory and statistics including the description and length of roads, type of pavement, width of shoulder, type of land, level crossing of railroads, sight distance, inclination, capacity information and the other important information. However, through Highways Information System (HIS) which based its studies on Geographical Information System (GIS) it is aimed at accessing correct information and data easily.
Estimations:
Estimations are necessary to define if project can meet the needs of future users with the current infrastructure and equipment, and whether additional investment is required or not by answering the questions such as, where, when, in which mode. Therefore, the estimations are calculated separately for the current project and the alternative ones.
Studies on Economical Analysis and Alternatives:
Project evaluation techniques which are internationally valid are used to search the benefits of project by comparing its cost- benefit with the help of economic analysis and to specify the priorities among them. These techniques are the most significant elements to specify the investment projects having priority. Decision maker authorities have to take into consideration the results of economical analysis as well as social interests and public opinions while choosing the project among alternative ones.
Formation and revision of projects and program by providing coordination between short- medium and long term plans and controlling their functioning have great importance.
SURVEY AND PROJECT STUDIES
 The first condition of constructing economical roads with high quality is to prepare projects with perfect surveys. Survey and project studies, therefore, carry great importance for General Directorate of Highways. Survey and project studies start after the Presidency of Strategy and Budget have ratified the roads included in the program through defining its feasibility and priority. First stage at the studies is to define alternative routes of decided roads by means of maps. Survey studies start by choosing the most appropriate one within the specified alternatives. While determining a route, one should consider the criteria such as; standards, cost, traffic, geological and geomorphologic structure of the area, landslide and drenage factors, social statue of the region. The project of the road is prepared, its quantity is defined, site plan of the bridges on the road are taken. Necessary band maps, plans and cross-longitudinal sections are prepared in the process of drawing road designs. In case a city passage different than intercity transportation exists on the route, its designing starts after the surveys related to the geological, topographical, economical structure of city, its traffic density, geographical situation, population and urban
structures are completed. Furthermore interchanges on the route of project are designed as level crossing or with bridges with the scale of 1/1000 by considering traffic surveys and taking into consideration the natural, economical and sociological factors.
Nowadays, designs are produced in the computerized environment creating a numeric area model in parallel with the developing technology as well as the projects of classical methods. Photogrammetry studies included in survey and design studies is a method to prepare healthier designs and maps and to carry out surveys with details. In the method of photogrammetry, air photographs supplied by General Directorate of Maps and private companies are used as data during the preparation of the project. During the survey and design studies, road route and alternative routes are determined just before the process of Environmental Impact Evaluation (EIE) of the road starts. Within the framework of the studies of Environmental Impact Evaluation (EIE), the description of project, the position of the place chosen for the project, economical and social dimensions of the project, current environmental, socio-economical features of the area to be effected by the project, the effects of the project on the area and the precautions to be taken, its effects on physical, biological and socio-economical environment during the phase of construction and operation and the precautions to be taken, the alternatives of the project have been examined with details by General Directorate of Highways within the scope of EIE report; and on one hand historical and natural environment are tried to be protected, on the other hand the project is assessed from the point of view of socio-economic environment and its effects on it, then they are benefited to make correct decisions.

TO FOLLOW AND IMPLEMENT HIGH TECHNOLOGY IN HIGHWAYS AND STUDIES RELATED TO QUALITY CONTROL
Highway construction is a special branch of engineering. It is important to carry it on scientific basis as well as following technological progress regularly. Furthermore, Technical Research Studies have incontrovertible function and importance regarding the facts above. These studies cover undertaking scientific research, collecting information on land and soil, searching for solutions for the problems probable to occur during the design and construction phases, following technical progress and implementing as well as conducting quality control. All those works and studies are based on the purpose of having our national road network acquired rational and economical qualities from the aspects of construction, maintenance and usage. It is necessary to research the appropriateness of the land regarding the physical features of soil where the route passes through, before the planned routes defined for the road construction are implemented on the land. To this end, Geological-Geotechnical surveys of “Corridor”, “Pre-Project” and “Final Project” are relatively performed. The most suitable one of designed routes is chosen taking into consideration its cost, adaptation to natural environment, geometrical standards, stability criteria regarding the processes of road construction and maintenance. Within the scope of these surveys landslide areas and marshy place passages on the land, nonqualified soil which can’t be used for fillings are investigated through geophysical and drilling works. If the critical points are found out works and studies are directed to solve their problems or search for new routes. At the end of the surveys, the maps which will be the base for the project are begun to be prepared for the confirmed routes. In case it is obligatory to construct the passage through the
areas of critical soil or landslide areas, advanced technological applications, such as, vertical drain, usage of geo-textile, ground nail, curtain walls with anchor-stakes, gabion walls, structure made of earth, are employed. During or after the production, advanced technology methods such as, inclinometer, piezometer, extensometer are used to inspect whether the values of project are realized or not. If necessary, project is revised and economical and safe passage is provided for the aforementioned sections. Tunnel surveys are carried out on the highway routes, research programs are prepared. Tunnel projects are prepared with the data collected. Observations and works realized during the tunnel construction are planned and assessed. Rehabilitation projects are prepared for the old tunnels. In tunnels observations and approach evaluation is performed by means of manometer, unit deformation poker, load cells, inclinometer, piezometer,
extensometer. A safe and economical tunnel is targeted benefiting the data collected through these measures.
Before the projects of road, bridge, viaduct, tunnel, foundations and structures are prepared, the characteristics of soil are found out. For this reason, surveys concerning to the mechanics of soil and rock and the foundation should be carried out, then the projects on this issue can be prepared. The basic purpose of our organization is to provide the construction of reliable
structures, it makes use of drilling machines, modern geophysical equipment and the laboratories of soil mechanics in its works. Designing of road pavement is an important study for the road construction. For this study, the standards related to the pavement thickness of the road to be constructed and the materials to spread out on the road are specified and overlay designs concerning to the pavement are prepared. Then surveys on the performance and bearing capacity of the pavement are carried out. Finally cause and solution of road deterioration are defined. Especially after the two big earthquakes, spectrum characteristics periods of soil are measured with Micro-Tremor studies contemporaneously with the developed
countries in order to safely design big structures of engineering. In the regulation concerning these values, reduction coefficients of aforementioned spectrum and earthquake load are calculated and tomography of related area is taken with GPR (geo-radar) studies, thus geological formations such as fault, bend, cavity existing underground are found out.
On the specified routes detailed geological and geo-technical surveys are carried out. Clefts and fillings are separately examined. During those works resources of natural construction materials necessary for road construction (quarry) are found out.
Geological-geotechnical reports of state roads and motorways, tunnel projects, pavement designs and reports related to quality control are either prepared or controlled by the Department of Technical Research. It is a condition that qualified materials in conformity with the standards should be used in road construction so that the roads will be long lived and of good quality. In the laboratories of our organization, quality controls of any kind of materials used for road construction are carried out and the physical, chemical and engineering qualities of the structures constructed with aforementioned materials at the construction stage are controlled as well. Then it is found out whether they are in conformity with standards and specifications. Finally the usage conditions are defined by means of the tests and experiments.
CONSTRUCTION WORKS
 When it is considered that the main duty of General Directorate of Highways is to reach the every corner of the country with roads; the significance of road construction for our organization is better understood. Since 1950 when General Directorate of Highways was established until 1970s, road construction by the General Directorate on its own gained importance as the private sector didn’t develop at that period. Construction works have been generally maintained through tender since 1970s for the contractor firms are developed. At this stage, the duty of General Directorate of Highways is to fulfill effective inspection service. General Directorate of Highways which constructs its own foundations as well as roads has taken over the construction of military and touristic roads in addition to the construction of state and provincial roads. New road construction, designed road maintenance, inter-city passages, touristic roads and private roads with protocol are included in the road construction works.
 The works on a new route consist of two steps: a) Substructure works: Substructure works include structure works, such as earth works, concrete pipe, culvert, retaining wall. Building bridges (including overpass & underpass) is involved in substructure works. b) Pavement works: Subbase, base, asphalt layer and concrete or parquet paving for special situations are included in the pavement works which follow the earth works. Today in the new highway understanding every kind of barrier construction, horizontal and vertical marking are included in the pavement works. In the period beginning from the foundation of Republic to 1960s the principle of “let wheels turn” was adopted, but then it was replaced with the understanding of roads with high quality, thus all kinds of innovations concerning to the pavement are began to be practiced in our country. The types of asphalt pavement used in our country are categorized as follows; bituminous surface treatment, cold mix asphalt pavement and bituminous hot mix asphalt. According to current highway understanding, bituminous surface treatment which was used in the first years of asphalt pavement (1960s) isn’t considered to be sufficient. Instead of it bituminous hot mix asphalt roads symbolizing the progress and modernization are preferred. Although the bituminous hot mix seems to be high costed at first sight, it is seen that it isn’t so high and it is sometimes much more economical when it is considered that it provides comfort to the driver and it gives service to traffic longer than the others (20 years according to the estimations based on project). It comes out as an obligation to take precautions to rehabilitate the geometrical and physical standards of the State Highways during the first decades of 2000s. According to the results of the capacity analysis depending on the increase in traffic (without considering the economical and social evaluations), it is targeted to upgrade the standards of State Highways under the responsibility of General Directorate of Highways during ten years between 1998-2008. These targets include that 6 350 km. of aforementioned highways will be turned into multi-lane road, 17 319 km. of them will be first class road, 7 651 km. will be second class; besides, 7 388 km. of State Highway carrying the heavy traffic burden of more than 1000 vehicles will be asphalt concrete pavement. The necessary importance will be given to construction of dual carriageway based on the feasibility surveys on the routes where required, by considering the highway transportation demand in our country and the balance between transportation
modes. Our organization has targeted to achieve 8000 km dual carriageway within the total state road network according to the work of “State and Provincial Road Standards for Planning Works 2000-2010”. The length of existing dual carriageway is 3424 km. It has been planned that 2000 km of the remaining 4576 km will be completed in short term, and its 2500 km will be constructed until 2010 regarding the priorities. However, the realization of the plans will be possible if the required finance resource is provided.
MOTORWAY WORKS
 The program of motorway construction has been put into practice by our organization in order to ease the traffic burden beginning to increase in 1980’s, significant progress was achieved. Motorway and connection road of total 92 km. has been completed in 2000 and 25 km. of which is opened to service. Today motorway and connection roads of 1 774 km. have been completed and opened to service, motorway of 1 092 km. under the same program has still been under construction. Although the motorway network was planned to reach 5000 km. by the end of last century, it reached to 2 866 km. due to the insufficient allocations for the motorways. In our country, the policy of financing motorway is based on using the toll revenues, external finance, revenues from various resources and national budget all together.

THE IMPLEMENTATION OF INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS
Non-Stop Tolling Systems on Motorways And
Bosphorus Bridges (NTS)
Traffic problems occur in the peak hours of the traffic especially in the big cities owing to rapid growth of population and the increase in the number of vehicle ownership in
Turkey. Within this context in order to prevent time loss and provide fast transportation, non-stop tolling system is
established and opened to service in 51 lanes and 19 toll plazas (21 entrance- 30 exit plazas). The number of registered substitute has exceeded 120.000.

NTS locations are as follows;
1. Division of General Directorate of
Highways
(Küçükyalı / İSTANBUL)
Çamlıca Station |
3 exit |
2 entrance |
Samandıra Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Kurtköy Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Şekerpınarı Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
2. Division of General Directorate of
Highways
(İZMİR)
Şehitlik Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Seferihisar Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Alaçatı Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Çeşme Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
17. Division of General Directorate of
Highways
(Zincirlikuyu / İSTANBUL)
Mahmutbey Station |
3 exit |
2 entrance |
Avcılar Station |
2 exit |
2 entrance |
Hadımköy Station |
2 exit |
2 entrance |
Kınalı Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Bosphorus
Bridge |
4 exit |
-- |
Fatih
S.
M.
Bridge |
3 exit |
-- |
Çatalca Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Selimpaşa Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Kumburgaz Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Çerkezköy Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
Çorlu Station |
1 exit |
1 entrance |
MAINTENANCE AND TRAFFIC WORKS

Maintenance work is as important as the construction work from the aspects of extending life of road and increasing its resistance to any kind of external impacts. Another aim of maintenance works is to provide a safer and comfortable travel for users in all weather conditions, so the smooth flow of traffic on road will be provided.
In our country the first maintenance works were conducted in 1948. Furthermore it has been accepted as a principle that maintenance of road is a necessity because just construction isn’t enough.
 The most important feature of maintenance works is that they should be conducted continuously. In case a downtime happens in maintenance works, serious deformation may occur due to weather conditions or heavy traffic. This leads to the increase in the maintenance and vehicle operating cost. Therefore, maintenance works should be carried out regularly within the framework of a program.
Maintenance works in highways are carried out by Divisions and their districts. Each district conducts the maintenance works and snow and ice removal with its own team within its boundaries.
Maintenance works can be classified as;
-routine maintenance -snow and ice removal
-maintenance in extraordinary situations.
Routine maintenance works include removing surface deformation on asphalt roads, corrugation and rutting on surface of stabilized road, repairing structures, such as, bridge, culvert, structures, also struggling against flow and erosion, clearing drenage systems, ditch and culverts as well as vegetation, etc.
Snow and ice removal has a considerable place in maintenance works. Removing snow and ice on roads during winter and providing a secure and smooth traffic flow are among these works.
Traffic works are also included in routine maintenance works. According to the traffic law with the number 2918, traffic works include making horizontal, vertical signs on roads under control of General Directorate of Highways in compliance with standards, conducting weight control and vehicle control effectively, conducting analysis on traffic accidents, preparing publications concerning the traffic training, specifying and removing black points in addition to traffic safety issues.
EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLY WORKS

Mechanized period for road construction started in 1948. Furthermore, until that time the roads had been constructed with human power. Thus fast and modern techniques were begun to be applied.
Before that period just trucks, rollers running on steam and fuel oil had been used in construction by General Directorate of Highways. In that period the number of machines increased. However, new problems, such as, absence of qualified personnel to operate these machines, to provide the required supply for their operation, to maintain and repair them, and the need for workshops and lack of personnel to conduct searches to purchase the machines and to draft specifications, occurred. Therefore, to solve the problems faced, technical units were formed in Headquarter and divisions. In this direction training about on operating the machines started, then required staff was trained and the amount of construction and maintenance equipment increased. As of January 1st, 2018 General Directorate of Highways has 11 871 equipment with the value of 615.086.737 US Dollar.
Taking into consideration the annual programs and inspecting the current construction and maintenance equipment, required machines are provided and the current ones are delivered and operated within the scope of equipment and supply works. Necessary workshops to repair and maintain them and telecommunication foundations are established. Then required machines, accessories and spare parts are manufactured or General Directorate of Highways gets them manufactured.
 Our organization pioneered the mechanized works. Furthermore, prototypes of required or export machines have been manufactured and mass production have started for the ones which have been produced successfully in our country.
Staff training programs about maintenance, operation and repair of machines belonging to General Directorate of Highways are permanently prepared.
Moreover, maximum and minimum stock amounts of every kind of machines, vehicles, devices, equipment and spare parts and their annual consumption amount, register and operation cost are fixed. Required ones are provided, stored and delivered.
Construction and Maintenance Equipment | Date
| Quantity
| Value ($)
| 01.03.1950
| 1 310
| 6 566 500
| 01.03.1960
| 10 308
| 55 435 600
| 01.03.1970
| 14 751
| 91 756 300
| 01.03.1980
| 17 931
| 160 534 400
| 01.01.1990
| 14 689
| 605 648 416
| 01.01.2000
| 12 664
| 545 976 844
| 01.01.2005
| 11 085
| 443 453 985
| 01.01.2006
| 11 220
| 476 503 092
| 01.01.2007
| 11 114
| 485 110 262
| 01.01.2008
| 11 249
| 523 245 316
| 01.01.2009
| 11 502
| 535 326 773
| 01.01.2010
| 11 342
| 544 199 197
| 01.01.2011
| 11 508
| 557 074 234
| 01.01.2012
| 11 555
| 573 953 792
| 01.01.2013
| 11 370
| 579 992 145
| 01.01.2014
| 10 477
| 556 672 996
| 01.01.2015
| 10 270
| 549 688 615
| 01.01.2016
| 10 198
| 549 530 354
| 01.01.2017
| 11 167
| 584 880 006
| 01.01.2018
| 11 871
| 615 086 737
|
BRIDGE WORKS
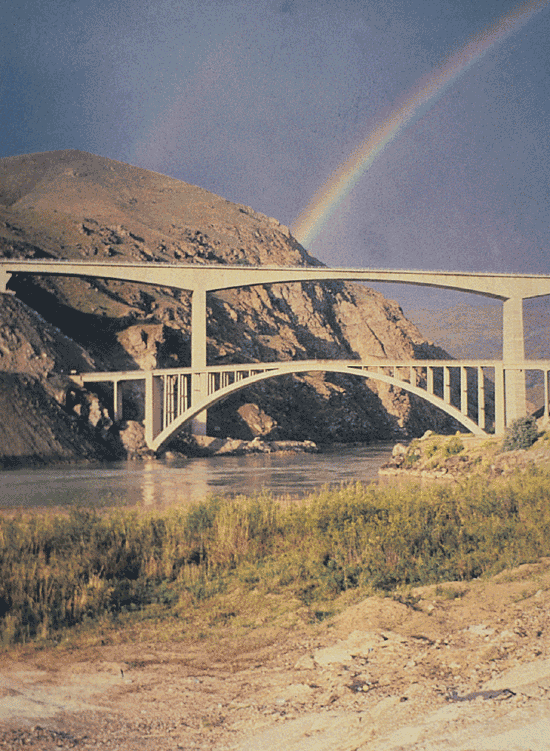 Bridge is another important structure on highways. After the establishment of General Directorate of Highways bridges were constructed in a modern way as a result of improvement in design methods and construction techniques.
Before the Republic period bridges had been wooden or built of stone. They had been narrow, had short span and low load capacity. In the Republic period reinforced concrete and steel bridges have been replaced the old ones. With the establishment of General Directorate of Highways construction of bridges gained momentum and pre-stressed reinforced concrete bridges are began to be constructed by means of new technologies in recent years. Long and high bridges are constructed especially over large rivers, dams' lakes and deep valleys with the latest technology in the world.
Within the framework of bridge construction works General Directorate of Highways prepares projects and technical specifications, then conducts the land and hydraulic surveys of bridges. Besides, it designs them or have the works done by means of tenders.
After the cost analysis is conducted, designed bridges are constructed in way of force account or tender in compliance with project, specification, contract and technical principals. During the construction work required technical controls, work program and other necessary operations are carried out by the organization.
In addition to maintenance and repair of bridges General Directorate of Highways also deals with the maintenance and restoration of historical ones, explains its view about the passage permission of trucks, etc. through the bridge. At the same time providing temporary panel bridges where the old one is out of service and preparing Program of Project and Survey for the new bridges, preparing the inventories of current ones are all included in the duties of General Directorate of Highways.
BRIDGES
Numbers and Lengths According to Years and Types |
Concrete |
Stone |
Composite |
Steel |
Total |
Number |
Length(m) |
Number |
Length (m) |
Number |
Length (m) |
Number |
Length (m) |
Number |
Length(m) |
4 370 |
167 277 |
120 |
6 386 |
320 |
13 013 |
36 |
1 601 |
4 850 |
188 277 |
|